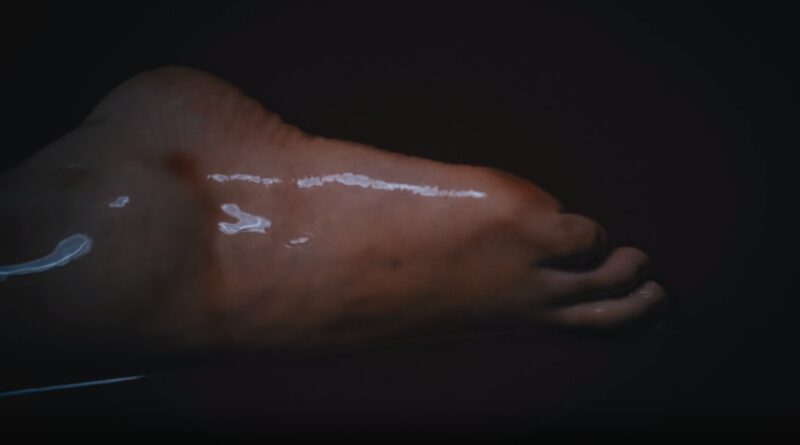
Gangrene: 5 Types You Should Know & Their Symptoms
Gangrene is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that arises when body tissues start dying due to insufficient blood supply. Recognizing the various types of gangrene and their symptoms is vital for early detection and swift medical intervention. Seeking immediate medical attention upon noticing any potential signs of gangrene is crucial, as timely intervention significantly improves the chances of successful treatment and recovery.
This article explores the characteristics of gangrene, emphasizing the importance of recognizing symptoms for effective treatment.
Types of Gangrene
Dry Gangrene: Dry gangrene is a common type that often affects extremities like fingers and toes. It happens when there is a substantial reduction in blood flow, resulting in the death of tissues. Symptoms include skin discoloration, pain, and a dry, shriveled appearance. It is essential to detect dry gangrene early to prevent further tissue damage, and treatment may involve improving blood circulation through medications or, in severe cases, amputation.
Wet Gangrene: Wet gangrene is characterized by bacterial infection and moisture, causing rapid tissue decay. This type can develop from an injury, infection, or other underlying health issues. Symptoms involve swelling, pain, and the release of foul-smelling discharge. Immediate medical attention is crucial, and treatment often includes surgical removal of the infected tissue and antibiotic therapy.
Gas Gangrene: Gas gangrene is a potentially life-threatening form caused by bacteria that produce toxins and gas within the affected tissue. This type of gangrene is characterized by severe pain, swelling, and the presence of gas bubbles under the skin. Urgent medical intervention is required, typically involving surgery to remove infected tissue and administration of antibiotics to combat bacterial infection.
Internal Gangrene: Internal gangrene occurs inside the body, affecting organs or internal structures. It may result from conditions like a compromised blood supply, infections, or injury. Symptoms may include abdominal pain, fever, and organ dysfunction. Early detection through imaging tests such as CT scans or MRIs is crucial for effective treatment, which may involve surgery to remove the affected portion.
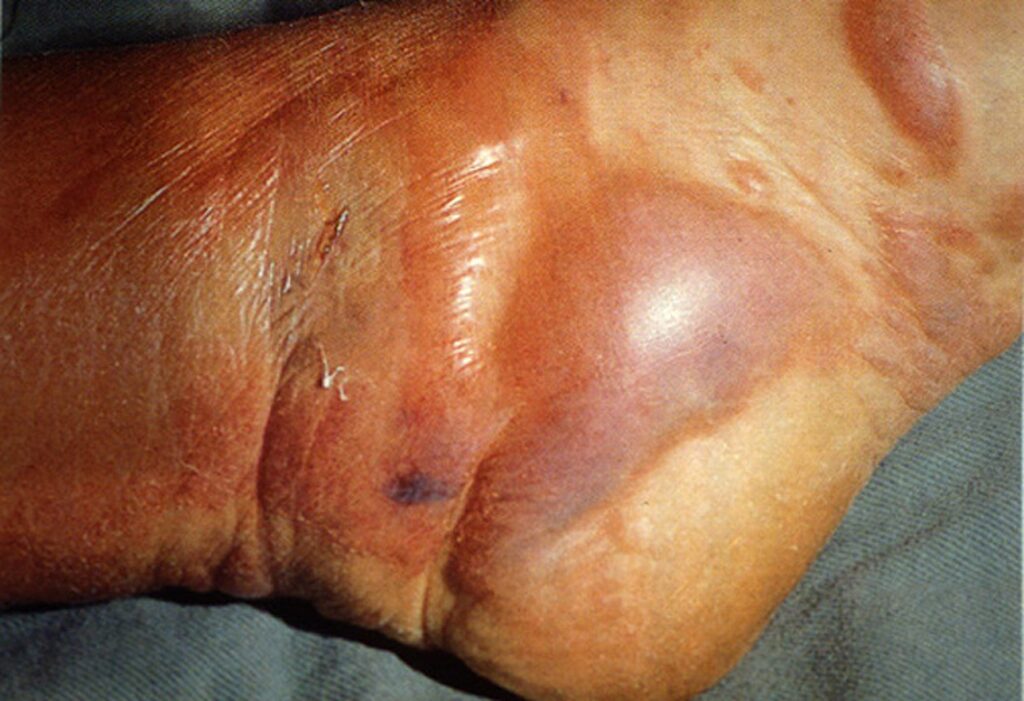
Fournier’s Gangrene: Fournier’s gangrene is a specific type that primarily affects the genital and perineal regions. It is a rare but severe condition more common in men and often associated with underlying health issues like diabetes. Immediate medical attention is necessary, involving surgical intervention and antibiotic therapy.
Fournier’s Gangrene: A Closer Look

Fournier’s gangrene requires special attention due to its unique characteristics and the severity of its impact on the genital and perineal areas. This rare condition demands immediate medical intervention, as its aggressive nature can lead to life-threatening complications.
Fournier’s gangrene symptoms are distinctive and require careful observation. Here are the symptoms:
Severe Pain: Patients afflicted with Fournier’s gangrene often endure excruciating and rapidly escalating pain in the genital and perineal areas. The pain is a prominent early symptom, signaling the aggressive nature of the infection. As the bacteria rapidly multiply and spread, the intensity of the pain can be debilitating, prompting individuals to seek medical attention urgently.
Redness and Swelling: The affected area undergoes a visible transformation as the infection progresses, manifesting as pronounced redness and swelling. This inflammatory response is the body’s attempt to contain the infection, but in the case of Fournier’s gangrene, it is often overwhelmed. The redness and swelling serve as visual indicators of the severity of the condition, emphasizing the need for immediate medical intervention to prevent further escalation.
Skin Ulcers: A distinctive feature of Fournier’s gangrene is the formation of skin ulcers in the affected regions. These ulcers may present as open sores or wounds on the skin surface, often accompanied by the discharge of foul-smelling fluid. The presence of ulcers signifies the advanced stage of tissue destruction, requiring specialized medical attention and intervention to halt the progression of the infection.
Fever and Systemic Symptoms: Fournier’s gangrene extends its impact beyond the local genital and perineal areas, affecting the entire body. Individuals with this condition commonly develop a fever, which is a systemic response to the invasive infection. Additionally, systemic symptoms such as weakness and fatigue may manifest, indicating the body’s struggle against the bacterial onslaught. Recognizing these systemic signs is crucial in assessing the severity of Fournier’s gangrene and underscores the urgency of seeking immediate medical care.
Treatment Options
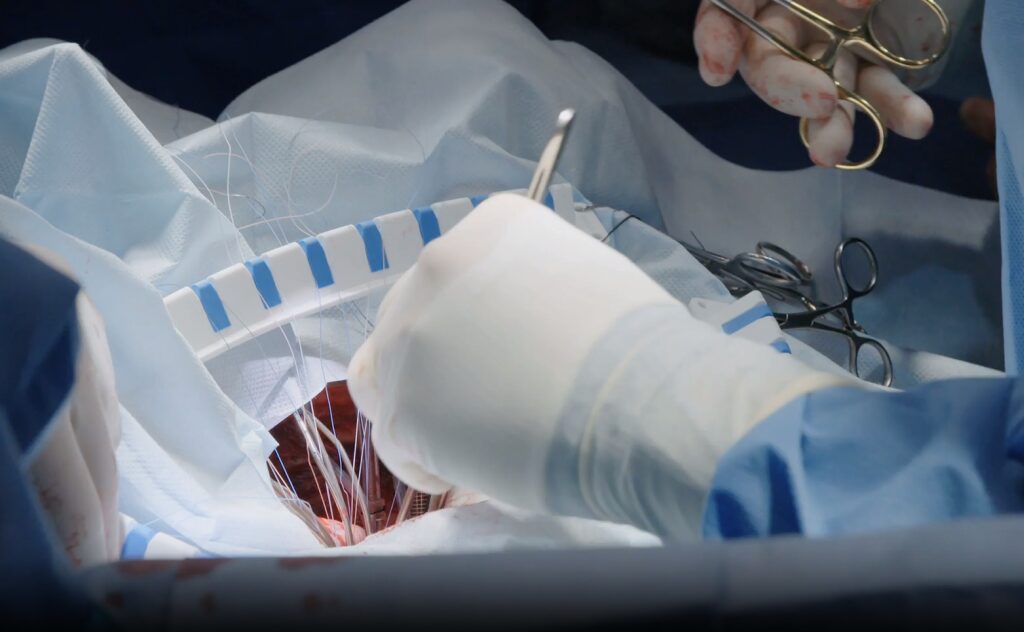
Treatment options for gangrene, including Fournier’s gangrene, are multifaceted and aim to address the underlying causes while preventing further tissue damage. In the case of dry and wet gangrene, interventions often include improving blood circulation through medications, wound care, and, in severe cases, surgical removal of the affected tissue.
Gas gangrene requires more aggressive measures, such as surgical debridement to remove dead tissue and the administration of powerful antibiotics to combat the bacterial infection. Internal gangrene may require surgery to remove the affected portion or address underlying issues causing compromised blood supply. Fournier’s gangrene, being a rapidly progressing and severe form, typically demands immediate surgical intervention, involving the removal of necrotic tissue and drainage of infected fluid.
Customized antibiotic treatment, designed for the particular bacteria responsible for the infection, plays a crucial role in treating various forms of gangrene. The severity of gangrene underscores the importance of early detection and prompt medical care, as treatment success is often contingent on timely intervention to halt the progression of tissue death and mitigate complications. Regular follow-up care is essential to monitor healing, manage potential complications, and ensure the best possible outcome for individuals affected by gangrene.
Understanding Severity
The severity of gangrene varies based on the type and how quickly it is addressed. Early detection allows for less invasive interventions and better chances of preserving affected tissues. Ignoring symptoms or delaying medical attention can lead to the need for more extensive procedures, including amputation in severe cases. It is crucial for individuals to understand the potential consequences of neglecting gangrene symptoms and to prioritize seeking medical help at the earliest signs of trouble.
Final Thoughts
Ultimately, gangrene is a serious medical condition that demands swift attention. Knowing the types and symptoms can aid in early detection and effective treatment. Timely intervention is crucial for preventing complications and preserving the affected tissues. If you suspect gangrene or experience symptoms, don’t hesitate—seek medical help promptly for the best possible outcome. Vigilance, early detection, and a proactive approach to seeking medical attention are key to addressing gangrene and its potential consequences.